Rt3072 Aircrack For Mac
After much frustration with this same problem I found a way to actually use Airodump on my Mac terminal. What I realized is that all of the files that I can successfully execute are located in the directory path /usr/local/bin/ And it turns out that Airodump was actually on my computer, it was just stored in the path /usr/local/sbin And I was unable to execute it from that path. All I did was move Airodump from the /usr/local/sbin path to the /usr/local/bin path and it now works great! I was going crazy for hours and it was that simple. As I don't have a running linix box at present I'm not up on the capabilities of aircrack-ng Possibles: iStumbler at Of the fairly sparse field,this one is probably the most current.
KisMac is a older port of Kismet last released in 2006, but reported to work on Snow Leopard. Haven't tried it. Another possible useful tool is WireShark. You will need to install XQuartz to use it, as it's an X11 windows app. A final possibility is to install windows under VirtualBox, Parallels or VMFusion and give it full access to your ethernet cards. Based on the clarification in your comment, I think wireshark would do what you want if you want to look at traffic.
If you just want to count packets, you can use netstat. This is a terminal program. (see man netstat) /Webwork/sftf 647 netstat -w10 input (Total) output packets errs bytes packets errs bytes colls 73 0 17551 77 0 11256 0 31 0 4731 41 0 6891 0 -w10 gives you a record every 10 seconds.
If you wanted hourly records you'd use -w3600. Netstat is general purpose. If you have multiple interfaces, you can filter to a given one with the -I flag. You can also do some filtering by protocol, address family. If you need serious filtering (I want to know how many packets bitorrent sent to the pirate bay last week) then you need either wireshark or tcpdump.
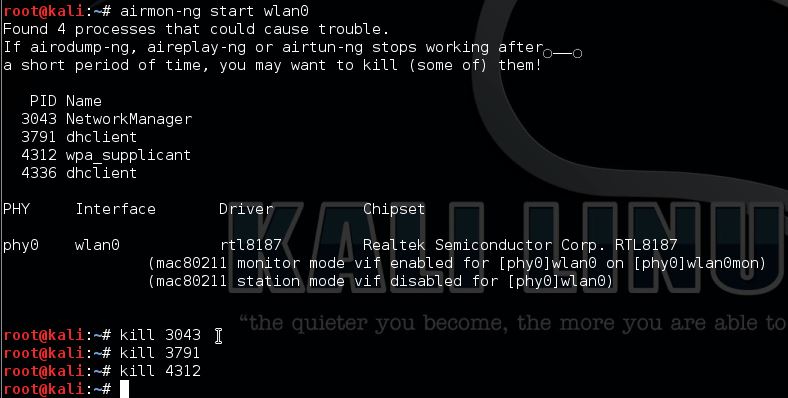
(Tcpdump is commandline) Wireshark is basically a GUI on top of tcpdump. Both have their place. I am using aircrack-ng on my mac, from the terminal, not emulating another OS.
Here is a good page mentioning the relation to other tools, which I think may help you: By the way, maybe you already have in the system what you are looking for: hidden in your airport is, from yosemite on, a sniffer. Press option and your wifi icon, you will see the option wireless diagnostics.
Rt3072 Aircrack For Mac Download
Games like silent hunter 5: battle of the atlantic for mac. Command 4 is scan (you see networks, channels, MACs, and other data) and command 6 is sniffer. Give that a try too.
Best greetings. It is possible to use enabled to essentially do the job of airodump-ng. This will allow for capture of raw 802.11 frames which will show the traffic from APs and clients. It needs to be remembered that the WiFi device can only listen on one channel at a time so you'll only see the traffic on the channel it's set to. You can choose the channel by associating a desired network before the capture or using the using the airport (/System/Library/PrivateFrameworks/Apple80211.framework/Resources/airport) command (e.g. To sniff channel 1 given your WiFi adapter is called en1): airport en1 sniff 1 Note that command this will also capture packets to file so one can just use airport to capture and then open the file in Wireshark or just quit the airport command after you have started monitor mode capture and let Wireshark collect them so you can see them in realtime.
One can actually change the capture channel whilst Wireshark is running but you may miss packets whilst the channel change occurs. Have you tried It has instructions to install aircrack-ng on Mac.
From the website: Installing on Mac OSX The simplest and easiest way to install on Mac OS X is via Macports. You simply do “sudo port install aircrack-ng”.

Alternatively, use the following instructions: Make sure you have Xcode installed on your Mac, which can be found on the installer CD/DVD which came with your Mac. After getting the source you can do a simple “make && sudo make install” from the untarred directory. When you use the stable, you need to rename the Makefile.osx to Makefile and when you use the dev version it will autodetect you are using Darwin and compile fine. Mind you, airodump-ng and aireplay-ng are linux only and will not work under OSX native, so for reinjecting and sniffing you will have to use other means. If you have an intel Mac check out the VMware Fusion option which is mentioned lower on this page. Optional is openssl-dev and sqlite3 which can be installed through fink.